Quadriceps Tendon Autograft
The quadriceps tendon autograft is the third type of autograft used for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction.
—– Learn more about the other graft types here —–
Although the use of this graft was first described in 1979, it has not been widely used until more recently. The most recent surveys show that worldwide, this graft is used about 10% of the time (2014) but <1% of the time in the US and Canada (2017).
It involves harvesting a 9-11 mm diameter graft from the central portion of the quadriceps tendon just above the patella (kneecap). It can be harvested with a bone block from the patella (shown as “Quad-Patella Bone” in the diagram below), or simply taken as a soft tissue graft as the tendon is long enough to be used alone. Like the patellar tendon, the quadriceps tendon has the potential to fully regenerate after harvest.
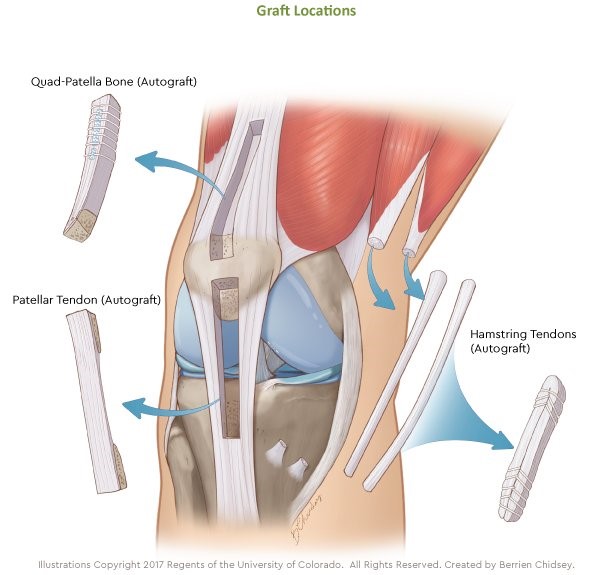
Advantages of the quadriceps tendon autograft

One of the main advantages of this graft is that the quadriceps tendon is large enough to provide consistency and predictability with regard to graft size, even in the small female.
It has a larger cross-sectional area than a patellar tendon graft and is also biomechanically superior in terms of strength and stiffness. Most studies show that there is significantly less anterior knee pain and kneeling pain than after ACL reconstruction with patellar tendon, as well as less impairment of quadriceps muscle strength recovery.
It also has a low incidence of skin numbness (<5%) and is a good autograft option to consider when performing a revision (re-do) surgery for a torn ACL graft because of its large size.
Disadvantages of the quadriceps tendon autograft
One of the main disadvantages of this graft is that it is more difficult to harvest for surgeons who have not had much experience with it. Most surgeons are more proficient in using hamstring or patellar tendon autographs, so they may have less success with the quadriceps tendon graft.
However, studies comparing quadriceps tendon autograft to hamstring tendon autograft and patellar tendon autograft, performed by surgeons who routinely use this graft, consistently show no significant difference in outcomes.
Another disadvantage is that there is the potential for a fracture of the patella to occur if a bone block is included in the graft. One case series by an experienced surgeon showed a patellar fracture rate of 8%, although it is important to note that only one of those patients had an unacceptable outcome. Moreover, including a bone block from the patella is seen as an advantage in terms of faster graft healing by some surgeons.
A minor disadvantage is that the incision can be quite long (similar to patellar tendon harvest incision), although the recent development of newer surgical tools allows for a much shorter incision.
Contributing expert

Dr Greg Buchko, Orthopaedic Surgeon







